一、单向链表
1.1 单向链表
链表是一种线性结构,通过一个链把所有的节点都链起来,因此叫做链表。它和数组最大的不同是:数组的内存是连续的,而链表不是。数组支持随机读写,但是插入和删除麻烦,链表不支持随机读写,但是插入和删除很方便。在更多场景下,链表用途更广。
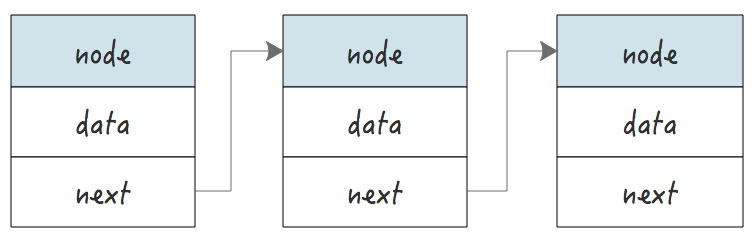
一个链表的图形示例如下,每个链表节点都包含了一个数据域和指向下一个节点指针:

链表是由一系列的节点构成,从面向对象角度来说,链表和节点是两个完全不同的东西。节点是链表中的实体,而链表只是节点的抽象,它包含若干个组成链表的节点。因此,链表和节点这两个对象应该区别开来。
一个基本的单向链表支持的操作:
- 添加节点
- 删除节点
- 查找节点
1.2 节点定义
一个节点的结构至少应该包含必要的数据域和 next 指针域,next 只用用于指向下一个节点的地址。
以下是一个最简单的链表节点示例:
链表节点的 C++定义:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
template<typename T> class list_node { // 友元类,方便链表类读取节点元素数据 friend class singly_linklist<T>; private: T data; // 数据域 list_node<T> *next; // 下一个节点指针 }; |
1.3 链表定义
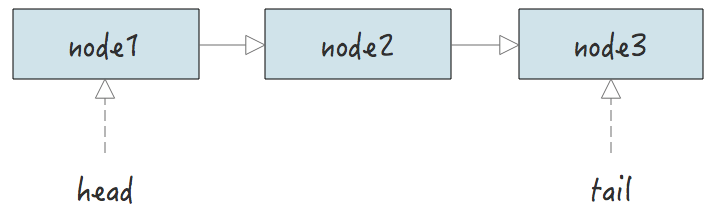
链表是由一个个的节点构成,在它的内部只要保存链表头节点的地址,就能找到链表中所有节点地址。
因此一个链表中,只要包含头结点的地址就行了。然后根据其他的扩展,我们可能还需要用到:
- 长度字段:O(1) 的时间复杂度返回链表长度。
- 尾结点指针:保存末尾节点的指针,尾插时 O(1) 的时间复杂度即可定位到尾结点。
链表的结构示意图:
链表的 C++定义:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
template<typename T> class singly_linklist { public: singly_linklist() : len(0), head(nullptr), tail(nullptr) {} private: size_t len; // 链表长度 list_node<T> *head; // 头结点 list_node<T> *tail; // 尾结点 }; |
所有代码使用 C++完成,后面的函数无特殊说明都是类成员函数。
二、插入节点
2.1 插入逻辑
以下图为例,不考虑首尾节点状态以及插入位置,一个节点被插入的逻辑是:
- 设置新增节点 node2 的 next 指向为 node3
- 修改原节点 node1 的 next 指向新节点 node2
- 插入完成
在链表类中,定义一个私有的添加节点函数 add_node 来完成这个插入操作:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
/* * 添加节点操作,新添加的节点需确保不是空值 * @new_node 新节点,不能为空 * @prev 前驱节点,可能为空 * @next 后继节点,可能为空 */ void add_node(list_node<T> *new_node, list_node<T> *prev, list_node<T> *next) { if (new_node == nullptr) return; len++; // 长度加 1 new_node->next = next; if (prev) { prev->next = new_node; } } |
2.2 头插法
头插法的意思是把节点插入到链表头部,这种情况下除了插入节点到链表中,还要注意的是修改链表的 head 节点指针。
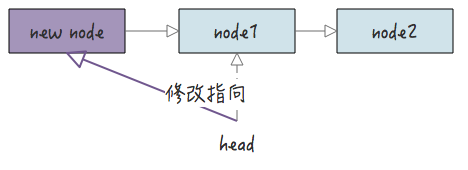
头插法函数实现:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
/* * 插入数据到链表开头 * @node 待插入的数据节点 */ singly_linklist &push_front(list_node<T> *node) { if (node == nullptr) return *this; // 添加节点到头部 add_node(node, nullptr, head); // 修改首尾节点指针 head = node; if (tail == nullptr) tail = node; return *this; } |
2.3 尾插法
尾插法和头插法相对,尾插法的意思是把节点插入到链表尾部,因此,插入后也要更新尾结点指针。
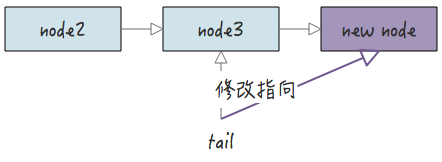
尾插法代码实现:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
/* * 插入元素到末尾 * @node 待插入的数据节点 */ singly_linklist &push_back(list_node<T> *node) { if (node == nullptr) return *this; // 插入节点到链表尾部 add_node(node, tail, nullptr); // 更新首尾结点指针 tail = node; if (head == nullptr) head = node; return *this; } |
三、查找元素
3.1 查找指定值的节点
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
/* * 在链表中查找指定值的节点 * @data 待查找节点 * @return 找到返回对应的节点,否则返回 nullptr */ list_node<T> *find(const T &data) { list_node<T> *p = head; // 遍历链表 while (p) { // 找到了 if(p->data == data) return p; // 没找到,继续找下一个 p = p->next; } return p; } |
3.2 查找指定节点的前节点
在增加或删除节点之前,都要修改前节点的指针指向,因此,需要实现一个查找指定节点的头结点函数。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
/* * 查找某个节点的前一个节点 * @node 当前节点 * @return 如果存在上一个节点,返回上一个节点的地址,否则返回 nullptr */ list_node<T> *find_prev(list_node<T> *node) { list_node<T> *p = head; if (node == nullptr) return nullptr; while (p != nullptr) { if (p->next == node) { return p; } p = p->next; } return p; } |
四、删除元素
4.1 删除逻辑
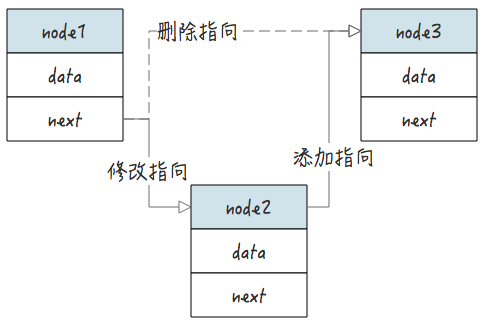
以下图为例,删除节点 2 的操作是:
- 修改节点 1 的 next 指向 node3
- 删除 node2 的 next 指向,删除完成
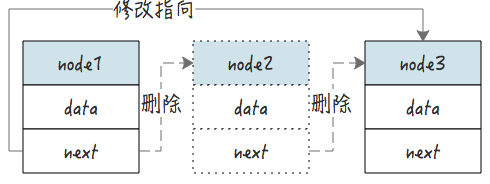
核心的删除代码:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
/* * 删除节点,待删除的节点请确保不是空值 * @del_node 待删除节点,不为空 * @prev 前驱节点,可能为空 * @next 后继节点,可能为空 */ void remove_node(list_node<T> *del_node, list_node<T> *prev, list_node<T> *next) { if (del_node == nullptr) return; len--; // 链表长度减 1 del_node->next = nullptr; // 被删除节点的 next 指针置空 if (prev) { // prev 可能为空 prev->next = next; } } |
4.2 删除指定节点
删除节点的一种操作是找到前节点指针,同时要注意的是,删除节点可能导致首尾指针失效,要注意更新首尾指针。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
/* * 删除节点 * @node 待删除节点 */ singly_linklist<T> &remove(list_node<T> *node) { list_node<T> *prev; if (node == nullptr) return *this; // 找到前节点 prev = find_prev(node); // 修改首尾节点指向 if (head == node) head = node->next; if (tail == node) tail = prev; // 删除节点 remove_node(node, prev, node->next); delete node; return *this; } |
4.3 删除首尾元素
有了上面的删除指定节点函数之后,删除首尾元素的操作就变得非常简单了:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
// 弹出首元素 singly_linklist &pop_front() { return remove(head); } // 弹出尾元素 singly_linklist &pop_back() { return remove(tail); } |
五、单元测试
5.1 头插法测试
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
TEST(singly_linklist, push_front) { int i; singly_linklist<int> list; const list_node<int> *p; vector<int> v{1, 2, 3}; list.push_front(3).push_front(2).push_front(1); EXPECT_EQ(3, list.get_len()); p = list.get_head(); for (i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) { EXPECT_EQ(p->get_data(), v[i]); p = p->get_next(); } EXPECT_EQ(p, nullptr); } |
5.2 尾插法测试
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
TEST(singly_linklist, push_back) { int i; singly_linklist<int> list; const list_node<int> *p; vector<int> v{1, 2, 3}; list.push_back(1).push_back(2).push_back(3); EXPECT_EQ(3, list.get_len()); p = list.get_head(); for (i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) { EXPECT_EQ(p->get_data(), v[i]); p = p->get_next(); } EXPECT_EQ(p, nullptr); } |
5.3 查找前一个节点测试
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
TEST(singly_linklist, get_prev) { int i; singly_linklist<int> list; const list_node<int> *p; list_node<int> *node1, *node2, *node3; // 插入 3 个节点 node1 = new list_node<int>(1); node2 = new list_node<int>(2); node3 = new list_node<int>(3); list.push_back(node1).push_back(node2).push_back(node3); EXPECT_EQ(3, list.get_len()); p = list.find_prev(node1); EXPECT_EQ(p, nullptr); p = list.find_prev(node2); EXPECT_EQ(p, node1); p = list.find_prev(node3); EXPECT_EQ(p, node2); } |
5.4 删除节点测试
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 |
// 测试删除节点 TEST(singly_linklist, remove) { int i; singly_linklist<int> list; const list_node<int> *p; list_node<int> *node1, *node2, *node3; node1 = new list_node<int>(1); node2 = new list_node<int>(2); node3 = new list_node<int>(3); list.push_front(node1); list.push_back(node2); list.push_back(node3); // 删除中间节点 list.remove(node2); EXPECT_EQ(node1, list.get_head()); EXPECT_EQ(node3, list.get_tail()); EXPECT_EQ(node1->get_next(), node3); // 删除头节点 list.remove(node1); EXPECT_EQ(node3, list.get_head()); EXPECT_EQ(node3, list.get_tail()); EXPECT_EQ(node3->get_next(), nullptr); // 删除尾节点 list.remove(node3); EXPECT_EQ( list.get_head(), nullptr); EXPECT_EQ( list.get_tail(), nullptr); } |