来源:力扣 (LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
一、题目描述
给定一个链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。要求返回这个链表的深拷贝。
我们用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index]表示:
- val:一个表示 Node.val 的整数。
- random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引 (范围从 0 到 n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为 null 。
示例 1:
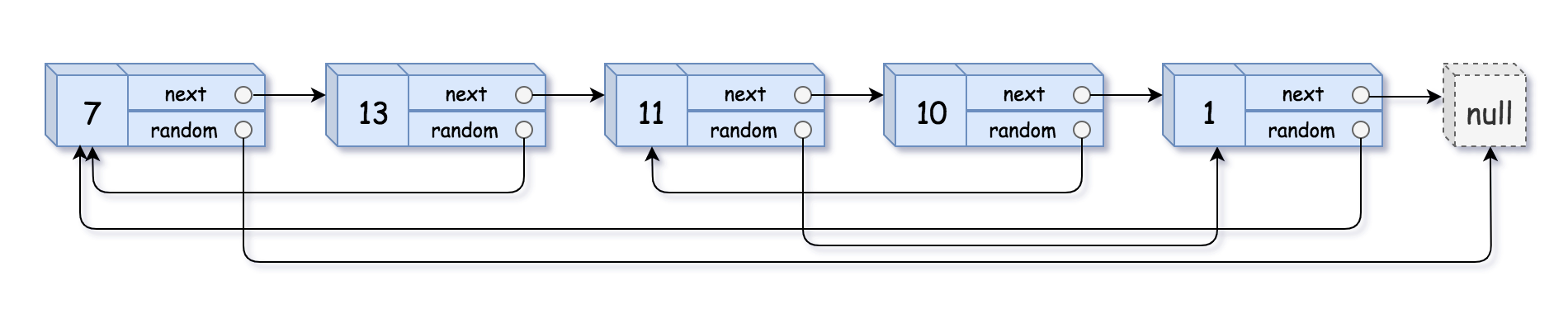
- 输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
- 输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
示例 2:
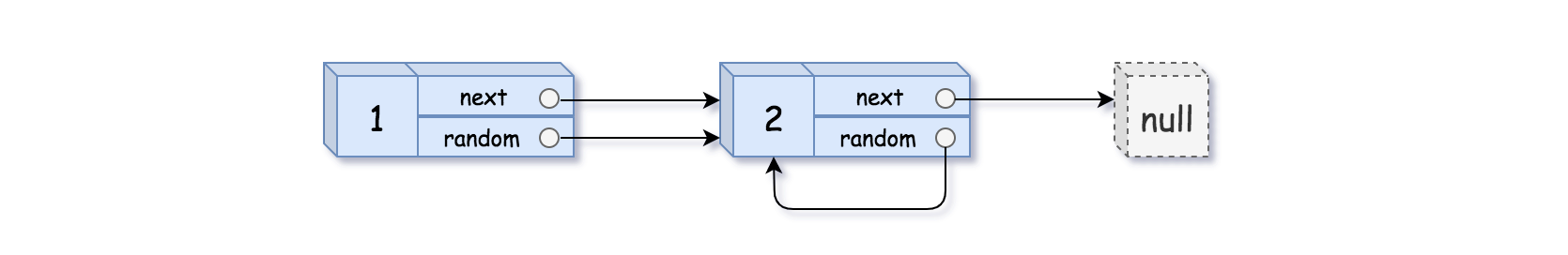
- 输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]]
- 输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
提示:
- -10000 <= Node.val <= 10000 。
- Node.random 为空 (null) 或指向链表中的节点。
- 节点数目不超过 1000 。
二、题目解析
《剑指 offer 》原题,详细解析 《剑指 offer 》面试题 35:复杂链表的复制。
三、代码
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 |
class Solution { private: /* * 克隆所有的节点,并串到原始节点中去 * @head 链表的头结点 */ void clone_all_nodes(Node *head) { Node *node, *clone; node = head; while (node) { // 拷贝节点 clone = new Node(node->val); clone->next = node->next; clone->random = node->random; // 修改 p 节点的下一个节点指向新创建的节点 node->next = clone; // 移动 p 指针到下一个节点 node = clone->next; } } /* * 修正所有克隆节点的随机指针的地址 * @head 链表的头结点 */ void fix_random_nodes(Node *head) { // node/q 节点分别表示原始节点和被克隆的节点 Node *node, *clone; node = head; while (node) { clone = node->next; // 修正 q 节点的 random 指针,注意 random 可能为 null if (clone->random) clone->random = clone->random->next; node = clone->next; } } Node *reconnect_nodes(Node *head) { Node *node, *clone; Node *new_head = head->next; node = head; while (node) { clone = node->next; // 备份下一个节点的指针 node->next = clone->next; // 连接到新克隆的节点,注意 next 可能为 null if (clone->next) { clone->next = clone->next->next; } node = node->next; } return new_head; } public: Node *copyRandomList(Node *head) { Node *new_head; if (head == nullptr) { return nullptr; } clone_all_nodes(head); fix_random_nodes(head); new_head = reconnect_nodes(head); return new_head; } }; |